Online 3D printing service
Get instant online quotes on parts in over 80 metal and plastic materials. Free shipping on all US orders. ISO 9001:2015, ISO 13485 and AS9100D certified.Start A New 3D Printing Quote
STEP | STP | IGES | IGS | SLDPRT | 3DM | SAT | X_T | IPT files and more!
Privacy: All your files are secure with us. Read our privacy policy.Direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) is an industrial metal 3D printing process that builds fully functional metal prototypes and production parts in 7 days or less. A range of metals produce final parts that can be used for end-use applications.
Metal 3D printing technology is commonly used for:
- Prototyping in production-grade materials
- Complex geometries
- Functional, end-use parts
- Reducing metal components in an assembly
Metal 3D Printing Capabilities
Our basic guidelines for metal 3D printing include important design considerations to help improve part manufacturability, enhance cosmetic appearance, and reduce overall production time.
*At this time, Inconel 718 and Aluminum are the only materials available on our large format, X Line machine
Metal 3D Printing Materials Guide
Learn more about the direct metal laser sinter process and the available materials for DMLS 3D printing.

Compare Material Properties
| Materials | Resolution | Condition | Ultimate Tensile Strength (ksi) | Yield Stress (ksi) | Elongation (%) | Hardness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel (17-4 PH) | 20 μm | Solution & Aged (H900) | 199 | 178 | 10 | 42 HRC |
| 30 μm | Solution & Aged (H900) | 198 | 179 | 13 | 42 HRC | |
| Stainless Steel (316L) | 20 μm | Stress Relieved | 82 | 56 | 78 | 90 HRB |
| 30 μm | Stress Relieved | 85 | 55 | 75 | 88 HRB | |
| Aluminum (AlSi10Mg) | 20 μm | Stress Relieved | 39 | 26 | 15 | 42 HRB |
| 30 μm | Stress Relieved | 50 | 33 | 8 | 59 HRB | |
| 40 μm | Stress Relieved | 43 | 27 | 10 | 50 HRB | |
| Cobalt Chrome (Co28Cr6Mo) | 20 μm | As Built | 182 | 112 | 17 | 39 HRC |
| 30 μm | As Built | 176 | 119 | 14 | 38 HRC | |
| Inconel 718 | 20 μm | Stress Relieved | 143 | 98 | 36 | 33 HRC |
| 30 μm | Stress Relieved | 144 | 91 | 39 | 30 HRC | |
| 30 μm | Solution & Aged per AMS 5663 | 208 | 175 | 18 | 46 HRC | |
| 60 μm | Stress Relieved | 139 | 83 | 40 | 27 HRC | |
| 60 μm | Solution & Aged per AMS 5663 | 201 | 174 | 19 | 45 HRC | |
| Titanium (Ti6Al4V) | 20 μm | Stress Relieved | 153 | 138 | 15 | 35 HRC |
| 30 μm | Stress Relieved | 144 | 124 | 18 | 33 HRC |
20 μm = high resolution (HR)
30, 40, and 60 μm = normal resolution (NR)
These figures are approximate and dependent on a number of factors, including but not limited to, machine and process parameters. The information provided is therefore not binding and not deemed to be certified. When performance is critical, also consider independent lab testing of additive materials or final parts.

Standard Finish
Expect roughness values of 200 to 400 µin Ra (0.005 to 0.010mm Ra), depending on material and resolution. Support structures are removed and layer lines are visible.

Custom Finish
We offer brushed surfaces in a range of grits and polished mirror finishes. Be sure to indicate if the custom surface finish is for functional or aesthetic purposes so we can best consult you on our custom options.
Post-Processing Capabilities for Metal 3D-Printed Parts
Improve strength, dimensional accuracy, and cosmetic appearance of final metal components with DMLS for production.
Surface Finishing
- 3- and 5-axis milling
- Turning
- Polish (Mirror or Brushed)
- Passivation
- Wire EDM
- Tapping and reaming
Heat Treatments
- Stress relief
- NADCAP heat treatment
- Hot isostatic pressing (HIP)
- Solution annealing
- Aging
Mechanical Testing
- Tensile
- Rockwell Hardness
Powder Analysis & Material
- Traceability
- Chemistry
- Particle size and distribution analysis


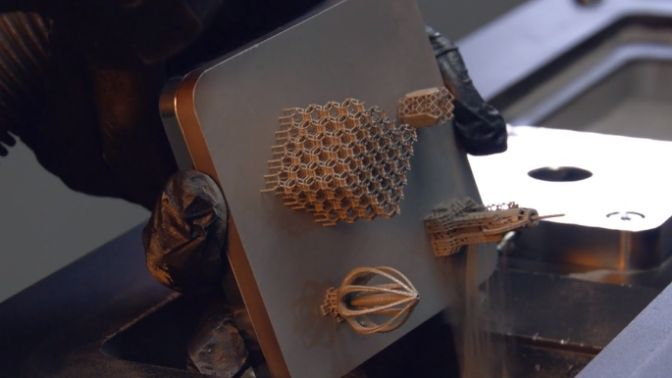
Why Use Metal 3D Printing?
See how metal additive manufacturing technology can be used to reduce components within an assembly, fabricate complex geometries, and ultimately save you time and costs.
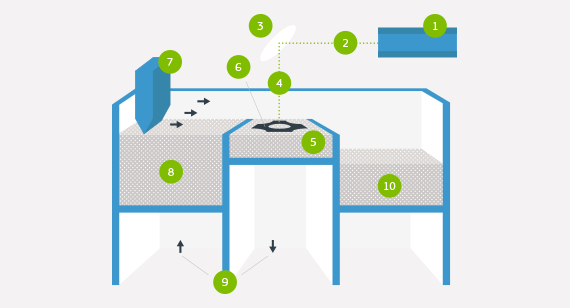
How Does Metal 3D Printing Work?
The DMLS machine begins sintering each layer—first the support structures to the base plate, then the part itself—with a laser aimed onto a bed of metallic powder. After a cross-section layer of powder is micro-welded, the build platform shifts down and a recoater blade moves across the platform to deposit the next layer of powder into an inert build chamber. The process is repeated layer by layer until the build is complete.
When the build finishes, an initial brushing is manually administered to parts to remove a majority of loose powder, followed by the appropriate heat-treat cycle while still fixtured in the support systems to relieve any stresses. Parts are removed from the platform and support structures are removed from the parts, then finished with any needed bead blasting and deburring. Final DMLS parts are near 100 percent dense.